The recent rollout of iOS 18 introduces a groundbreaking Messages via Satellite feature, specifically designed for the iPhone 14 series, which promises to profoundly alter how users stay connected in remote locations devoid of traditional cellular networks. This innovation not only broadens the horizons of communication but also prioritizes safety by ensuring messages can be sent during critical situations. However, as users begin to navigate this new terrain, questions about the practicality of its application, such as the impact of transmission speeds on communication effectiveness, remain. Understanding these nuances is essential for users who may depend on this technology in unforeseen circumstances.
Unveiling Satellite Messaging
iOS 18 marks a significant advancement in mobile communication with the introduction of Messages via Satellite, enabling users of iPhone 14 and later models to send and receive texts in areas devoid of traditional network coverage. This new feature caters specifically to ensuring that individuals remain connected even in the most remote or challenging environments.
Satellite messaging through iOS 18 is not just a leap in geographical coverage; it also integrates robust privacy measures. The service supports end-to-end encryption, safeguarding the privacy and security of communications, irrespective of the user’s location.
Through Messages via Satellite, users can exchange iMessages, SMS texts, emojis, and tapbacks, all encrypted from sender to receiver. This move by Apple not only enhances connectivity but also reinforces its commitment to user privacy.
Initially rolled out in the United States, Messages via Satellite aims to bridge communication gaps caused by natural disasters or other emergency scenarios where conventional networks fail. The technology is designed to be seamlessly integrated within the existing Messages app, providing an intuitive user experience without the need for additional software or complex configurations.
This feature underscores Apple’s initiative to merge cutting-edge technology with practical, user-focused solutions.
Operational Mechanics Explained
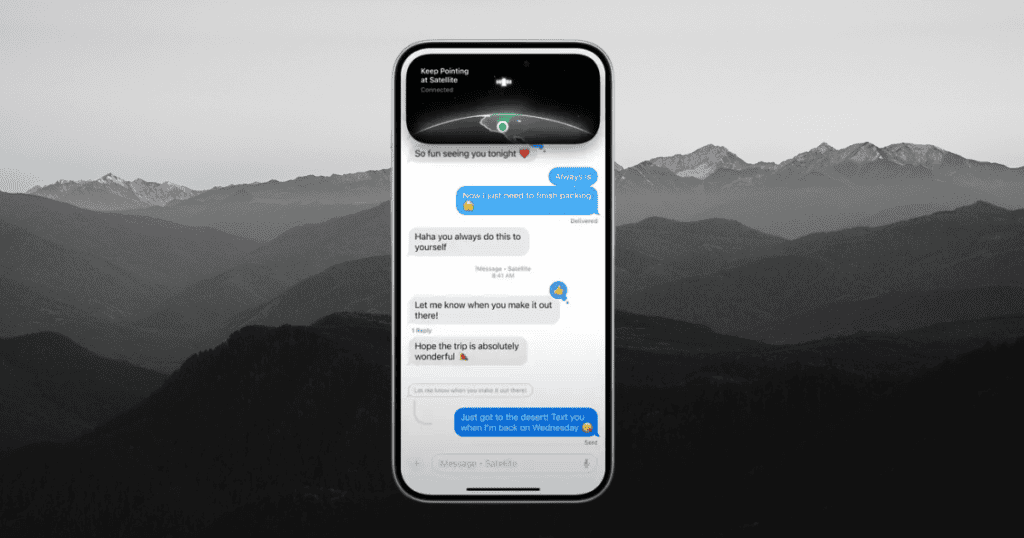
Understanding the operational mechanics of Messages via Satellite is key to maximizing its effectiveness and ensuring reliable communication in remote areas. When users send messages via satellite using iOS 18, they must be aware of the slower transmission speeds compared to standard messaging. Typically, messages sent via this method take about 15 seconds to deliver, though this can be delayed by physical obstructions such as dense foliage or buildings.
To facilitate a successful connection, users are required to maintain a clear line of sight between their device and the sky. The system prompts users with onscreen instructions to help position the device for best satellite reception. This may include moving to locations with less obstruction or adjusting the orientation of the iPhone to align better with satellite signals.
Furthermore, all messages sent via satellite are end-to-end encrypted, ensuring that communication remains secure and private. This encryption is implemented through a custom protocol designed specifically for satellite messaging, enhancing data security even in the most remote locations.
Coverage and Accessibility
The introduction of Messages via Satellite in iOS 18 greatly extends coverage, enabling users to communicate securely in remote areas where traditional networks fail to reach. This innovation leverages the satellite capabilities on iPhone, providing an important connection point during emergencies or in geographically isolated locales.
The ability to send and receive messages via satellite guarantees that users maintain communication lines without reliance on terrestrial infrastructure. However, it’s worth noting that while iMessages can be fully utilized, the feature has limited SMS capabilities, focusing primarily on essential and emergency communications.
To illustrate the breadth and functionality of this new feature, here is a detailed breakdown:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Satellite Access | Enabled globally for iOS users in remote locations. |
| Message Types | Supports iMessages and limited SMS. |
| Encryption | End-to-end encryption ensures secure communications. |
| User Accessibility | Simple interface via the Messages app. |
| Launch Regions | Initially available in the United States. |
This table highlights the key aspects of the Messages via Satellite feature, showing how iOS 18 is set to revolutionize communication for users in underserved areas, enhancing both reach and security.
Limitations and Speed
- Broadened Communication Capabilities: Messages via Satellite in iOS 18 significantly expands communication reach.
- Users must adjust expectations due to inherent limitations and slower speeds.
- Transmission Speeds and Obstructions: Typical message delivery through satellite takes around 15 seconds.
- Delays can extend to over a minute if obstructed by buildings or trees.
- Slower transmission rate is notable compared to near-instantaneous delivery via cellular networks.
- Content Limitations: Satellite messaging supports text-only communications.
- Does not support sending of photos, videos, or group chats.
- Primarily designed for basic communication needs in remote or underserved areas.
- Performance Requirements: Users need to be outdoors with a clear line of sight to the sky for optimal performance.
- Precise following of on-screen instructions is crucial for maintaining a stable satellite connection.
- These requirements emphasize the need for careful planning when relying on satellite messaging.
Emergency Use Cases
Emergency use cases for Messages via Satellite in iOS 18 enable critical communication with first responders when conventional methods fail. This innovative feature fundamentally transforms how individuals can reach emergency services, particularly in scenarios where traditional network infrastructures are compromised or non-existent.
Whether due to natural disasters, extreme weather conditions, or remote location challenges, iOS 18 guarantees that users can send and receive messages directly to and from first responders via satellite connections.
The functionality of emergency SOS via satellite is tailored to prioritize messages during crisis, facilitating a faster response when time is critical. By providing a direct line to emergency personnel, users are afforded a significant safety net that transcends the limitations of cellular networks. This capability is especially vital in areas where cell towers are damaged or entirely absent, securing a lifeline for those in dire situations.
Apple’s commitment to integrating satellite communication for emergency use cases underscores a proactive approach to public safety. It ensures that users have access to emergency assistance with greater reliability, emphasizing the importance of connectivity in life-threatening situations.
This development not only enhances personal security but also bolsters the overall efficacy of emergency response strategies globally.
Comparing Traditional SMS
Traditional SMS messaging, reliant on cellular networks, contrasts with iOS 18’s satellite messaging, which offers connectivity in areas devoid of cellular service. While SMS is a well-established mode of communication that allows for instant message delivery under normal network conditions, its dependency on cellular infrastructure can be a limitation. Users in remote or poorly covered areas often experience delays or message failures, which can be critical during emergencies.
Conversely, iOS 18 introduces a significant enhancement to the iPhone’s Messages app with the integration of satellite connectivity. This feature is particularly valuable in situations where cellular networks are compromised or non-existent. However, it is important to note that while satellite messaging provides a critical communication link in such scenarios, it does not offer the same speed as traditional SMS. Messages sent via satellite may take longer to transmit, reflecting the inherent limitations of current satellite technology.
Despite these differences, the ability to send messages through satellites adds a layer of reliability and accessibility that was previously unavailable to iPhone users. This development not only broadens the scope of communication possibilities but also underscores the commitment to safety and connectivity in the evolving digital landscape.
Future Enhancements Expected
Looking ahead, future enhancements for Messages via Satellite may support calls and multimedia content, greatly expanding the utility of this innovative service. As iOS continues to evolve, these new features could allow users to send and receive not only text but also images, videos, and voice recordings via satellite. This would be especially beneficial in remote areas where traditional communication methods are often unreliable or unavailable.
Apple is likely to further develop this technology to include a broader range of communication options, making it an even more indispensable tool for adventurers, travelers, and those living in underserved regions. The ability to place calls through satellites could revolutionize how we think about mobile connectivity, particularly in emergency situations where immediate voice contact is essential.
Moreover, adding such capabilities could provide significant financial benefits for Apple. As these advanced features enhance the overall user experience, they could incentivize consumers to upgrade to newer iPhone models that support enhanced satellite communication services. This would not only boost iPhone sales but also strengthen brand loyalty among users who rely heavily on mobile connectivity for their personal and professional lives.
The continual expansion of iOS satellite capabilities marks an exciting chapter in mobile communications.
MacReview verdict
To sum up, the introduction of Messages via Satellite in iOS 18 represents a pivotal shift in mobile communication technology, offering unprecedented connectivity in remote areas.
Despite limitations in speed and content type, the capability to send encrypted texts via satellite vastly enhances safety and accessibility.
How might future enhancements further revolutionize our communication landscape, particularly in underserved regions?
Continued advancements are anticipated to refine and expand this innovative feature, ensuring broader applicability and user convenience.