Apple is working on technology to simplify iPhone battery replacement that could debut later this year, The Information reports.
Response to EU Legislation
The move comes in response to a new EU law requiring smartphone manufacturers to ensure batteries can be replaced by owners using easily accessible tools by 2025. According to sources involved in the iPhone’s manufacturing process, Apple is exploring the use of electrically induced adhesive debonding technology to achieve this.
Current Battery Replacement Challenges
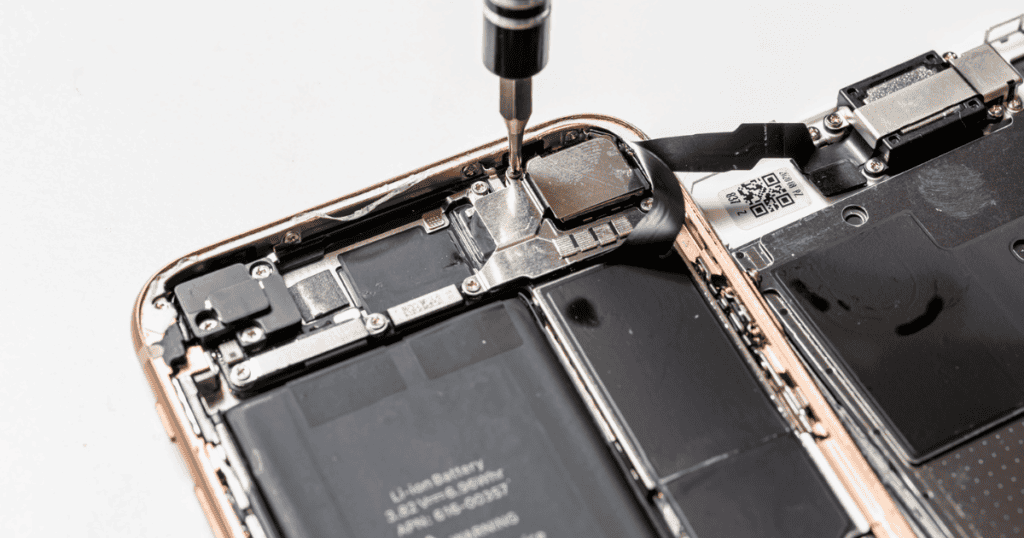
The current method of replacing an iPhone battery is challenging and involves removing adhesive strips with tweezers. If these strips break during the process, additional steps involving heat or solvents are necessary to dislodge the adhesive. After removing the old battery, a tray and specialized machine are required to install a new one securely.
New Technology: Electrically Induced Adhesive Debonding
In contrast, the new technology Apple is testing involves encasing the battery in metal rather than black foil. Alleged images of an iPhone 16 Pro battery with a metal casing leaked earlier this year. By applying a low voltage of electricity, the new battery can be quickly dislodged from the chassis. Despite this advancement, consumers will still need to open the iPhone themselves, which remains complicated due to the use of adhesives and screws to keep the iPhone’s display in place and retain water resistance.
Potential Release and Recommendations
This new battery replacement method is anticipated to debut in at least one iPhone 16 model later this year and could be extended to all versions of the iPhone 17 next year. Apple is expected to continue recommending that users seek professional assistance for battery replacements, given the complexities and potential risks associated with the procedure.
Compliance with EU Legislation
Apple may be exempt from the EU’s legislation requiring consumer-friendly battery replacement if its devices meet certain criteria, such as retaining 83% of their capacity after 500 full charges and 80% after 1,000 full charges. The iPhone 15 meets the criteria for 1,000 charges, but earlier models do not meet the 500-charge requirement.
Apple’s Repairability Initiatives
While Apple has a history of offering devices that are challenging to repair due to their tightly sealed designs which enhance water resistance and durability, the company has taken steps to address these concerns by introducing self-repair options and making diagnostic tools available in recent years.
Final Thoughts
Apple’s development of electrically induced adhesive debonding technology signifies a significant step towards more user-friendly and repairable devices. This innovation not only addresses upcoming EU legislation but also reflects a broader commitment to improving the repairability of its products. If successful, this technology will make battery replacements more accessible and less time-consuming for consumers, aligning with Apple’s ongoing efforts to enhance the user experience and sustainability of its products. As we await the official release, it’s clear that Apple continues to lead the industry in balancing advanced technology with practical usability.